In this article I would like to talk about the deployment of Office 365.
We can prepare, automate, customize, etc. a lot in our Microsoft Admin Portals.
Nevertheless, it happens again and again that parts of the service do not work. My experience has shown me that in more than 90% of the cases, one of these 2 points was responsible.
Firewall exceptions
During one of my last installations we deployed Microsoft 365 via autopilot. This basically worked very well. Only the office package could not be installed.
In another case, the Office applications were already installed, but could not be updated.
Both customers had one general thing in common. This was the used firewall. In this case we are talking about Sophos Astaro UTM.
I am not saying that this problem can only occur with a Sophos UTM firewalls, but in my example I am using that firewall.
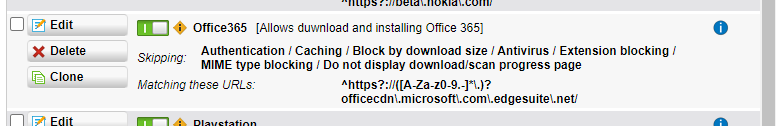
The reason why Office could not be installed is that the firewall requires an exception.
Here is how this can be done:
Note: Please note that this is only an example with a Sophos Astaro Firewall. Other vendors with similar issues will have similar procedures. What matters most is the information that this must be taken and what value we must use to make it work.
General Firewall Ports
Another possible reason for service problems with Office 365 can be the classic firewall ports.
I have already described the ports for Exchange and Skype for Business in more detail in a previous article.
In this part of my blog article I would like to keep it a bit more general, but you will still recognize some entries in the following list:
| Server/Service | Port | Protocol | Direction |
| ADFS (Internal) | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| ADFS (Proxy DMZ) or WAP Server | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Microsoft Online Portal (Website) | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Outlook Web Access (Website) | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Lync/Skype for Business Client | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| SharePoint Online (Website) | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Outlook for Mac | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Outlook Client | 443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Mail Routing | 25 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| SMTP Relay (requires TLS) | 587 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Simple IMAP4 migration Tool | 143/993 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| POP3 (requires SSL) | 995 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| DirSync/Azure Active Directory Sync | 80/443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Exchange Migration Tool | 80/443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| IMAP Migration Tool | 80/443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Exchange Management Console | 80/443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Exchange Management Shell | 80/443 | TCP | Inbound/Outbound |
| Lync (Data Sharing Sessions) | 443 | TCP | Outbound |
| Lync (Video, Audio, Application Sharing) | 443 | TCP | Outbound |
| Lync (Audio & Video) | 3478 | UDP | Outbound |
| Lync (Audio & Video) | 50000-59999 | TCP/UDP | Outbound |
| Lync Mobile Push iOS Only | 5223 | TCP | Outbound |
Conclution
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, these two chapters in this article cover over 90% of the problems that occur when Office 365 installations or updates fail.
I hope this article has helped some of them.
Photo by Maud Bocquillod on Unsplash