Microsoft sees midsize businesses as users of Office 365 and is setting things in motion to facilitate the migration of a local Exchange environment to the online office. For example, the Microsoft Hybrid Wizard with the Hybrid Agent has received an update that has been available since last February and was updated in April 2019.
The migration of mailboxes to Exchange Online is one of the major challenges when using Office 365 with all its features. For this reason it is important to make this step as easy as possible. Unlike migration within an organization, moving to Exchange Online is problematic because mailboxes are moved between two separately managed organizations.
The connection of an on-premises Exchange instance to Exchange Online is called a hybrid connection. The Hybrid Agent is a new tool to facilitate the connection. Microsoft calls this connection “Modern Hybrid” and thus extends the “Hybrid Configuration Wizard” (HCW). The new Hybrid Agent establishes a connection between the on-premises Exchange version and Exchange Online. In doing so, the Hybrid Agent reduces the requirements for external DNS entries, certificate updates and incoming network connections of the firewall, which made the task complex in the past.
Practical due to multiple installation
The Hybrid Agent does not support “Hybrid Modern Authentication”. This includes, for example, multi-factor authentication or authentication with client certificates. If this is already being used, continue to use the classic Exchange hybrid topology. Furthermore, MailTips, message tracking and multi-mailbox search are not handled via the Hybrid Agent. If these functions are to be used across the board, continue to use the classic model.
How Microsoft Hybrid Agent works
The Microsoft Hybrid Agent uses a URL in the following format for communication:
<guid>.resource.mailboxmigration.his.msappproxy.net
This URL is used to connect the on-premises Exchange infrastructure to Office 365. The organization’s mailbox replication service uses this URL for communication. The agent can currently only run on one server in the Exchange organization. However, Microsoft is working to make the agent highly available in the future.
Prerequisites for operating the Microsoft Hybrid Agent
For the Microsoft Hybrid Agent to work, it must be able to establish outgoing HTTPS connections to the Internet. To do this, the server must be allowed to communicate with the Internet via ports 80 and 443. If the agent is not installed on a server that provides the Client Access Service (CAS), it must be able to communicate with the CAS server over the network on ports 80, 443, 5985, and 5986.
Note: More about Exchange Ports you can find HERE.
Remote PowerShell (RPS) to the Client Access Service on the network must also be available. The server should have at least Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 installed and .NET Framework version 4.6.2 or later. Internet Explorer is required to install the agent.
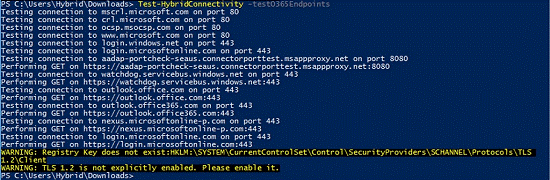
Microsoft provides a script to test the connection. The PowerShell script must first be imported into PowerShell as a module:
Import modules .\HybridManagement.psm1
You can then use the following cmdlet to test the connection:
Test HybridConnectivity -testO365Endpoints
Installation steps
- Log into your on-premises Exchange admin center (EAC), navigate to the Hybrid node, and then click Configure.
- Select the Exchange server where you want to run traditional hybrid setup. Either select the default server provided by the HCW or specify a specific server in the second radio button. Select Next.
- Enter your on-premises Exchange credentials and your Office 365 Global Administrator credentials. Click Next.
- Wait while the HCW gathers information and configuration about your environments. When it’s completed. Click Next.
- Select either Minimal or Full Hybrid Configuration. You can also choose Organization Configuration Transfer.
- Click Next
- Follow the steps to enable federation. Click Next
- Select Use Exchange Modern Hybrid Topology
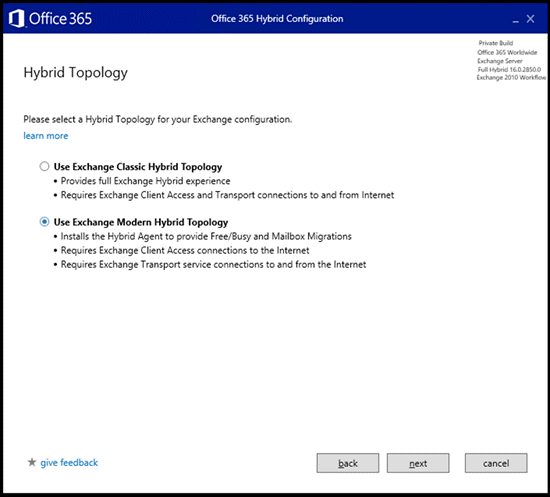 |
Click Next. |
- The HCW installs the Hybrid Agent. There are four basic phases:
- Download the agent install package.
- Installation of the agent on the local computer (note: this prompts for your Office 365 Global Administrator credentials again).
- Registration of the agent in Azure, including creation of the URL used to proxy requests. The URL has the format: uniqueGUID.resource.mailboxmigration.his.msappproxy.net.
- Testing migration viability from your Office 365 tenant to your on-premises Exchange organization via the agent.
The remaining HCW inputs and actions are the same as a Classic Hybrid deployment.
During the update phase, the HCW creates a migration endpoint with the custom URL created earlier. It will also set the TargetSharingEPR value on the Organization Relationship and/or the IntraOrganization Connector object on the Office 365 side to this value. The new URL is used to send requests from your Office 365 tenant to your on-premises Exchange organization for free/busy and migrations.
Additional Information
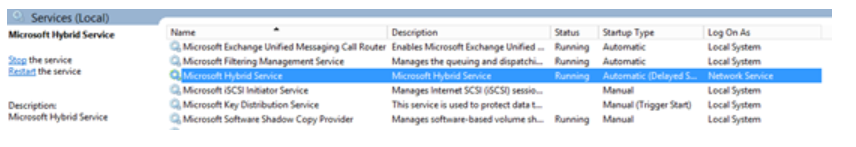
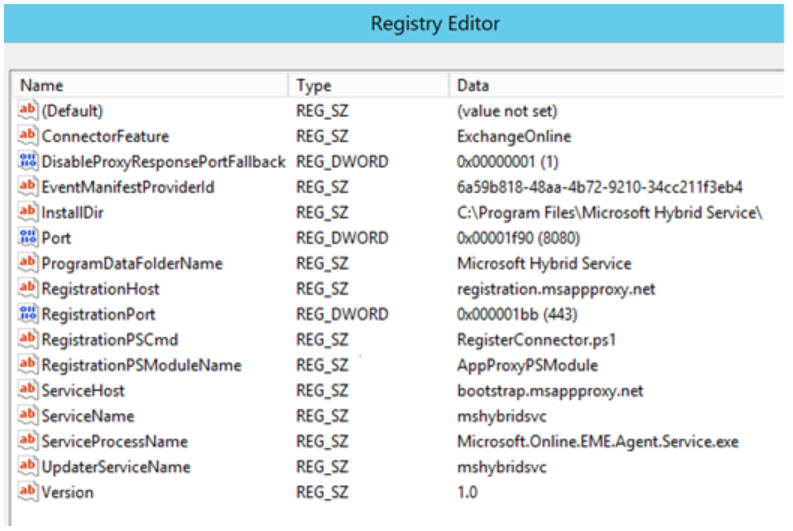
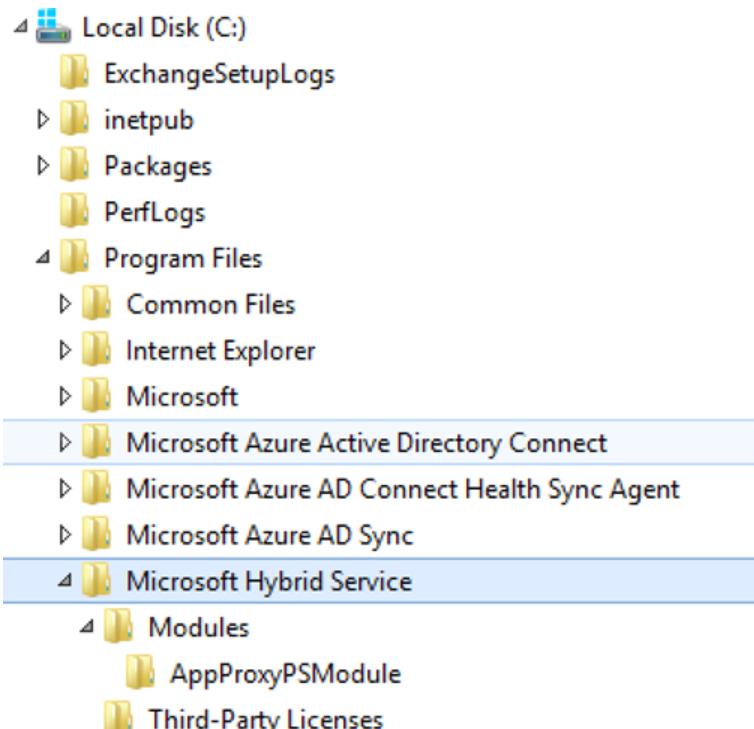
You can view installation details of the Hybrid Agent in the following locations on the server where it’s installed.
In the Services console:
In the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Hybrid Service:
On the hard drive:
Photo by Sandra Seitamaa on Unsplash